Investigations of Classical Communication-assisted Entanglement Sharing
Entanglement is a key resource in quantum information processing tasks. Thus, identifying the best attainable rates for sharing entanglement across noisy quantum communication links is a crucial question in the study of quantum computing and communication.
In this project, working with Vikesh Siddhu, Tomas Jochym-O’Connor, and John Smolin, we study entanglement sharing in the setting where the sender and receiver can also communicate classical messages. We study the amplitude damping channel, Pauli channels, and a practically relevant model that we call the damping-dephasing channel. For all these channels, we provide protocols achieving state of the art entanglement sharing rates. These improvements rely on the intuition gained by thinking about these protocols through the lens of an idea which we call channel reshaping. This work was done in part during an internship at IBM. More details can be found in the papers; here and here.

Interpolation of Quantum Polar and Reed-Muller Codes
Good quantum error-correcting codes that fulfill practical considerations, such as simple encoding circuits and efficient decoders, are essential for functional quantum information processing systems. Quantum polar codes satisfy some of these requirements but lack certain critical features, thereby hindering their widespread use. Existing constructions either require entanglement assistance to produce valid quantum codes, suffer from poor finite-size performance, or fail to tailor polar codes to the underlying channel properties. Meanwhile, quantum Reed-Muller (RM) codes demonstrate strong performance, though no known efficient decoding algorithm exists for them.
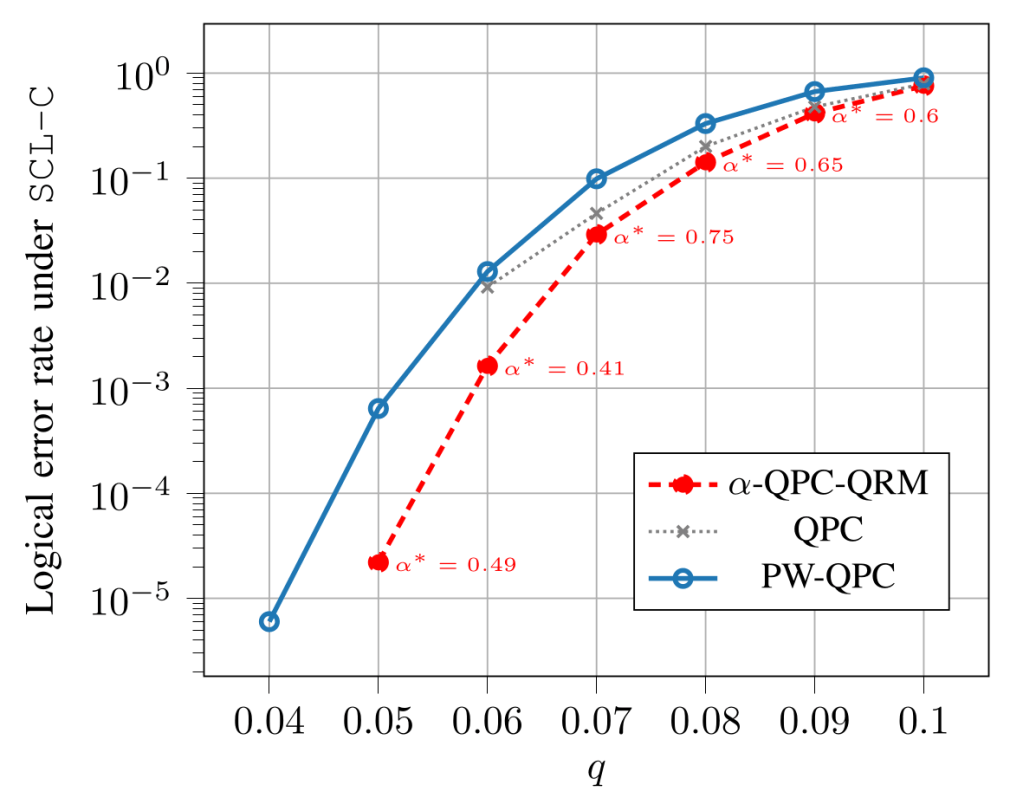
Working with Keita Hidaka and Ruediger Urbanke, we propose a quantum code construction interpolating between quantum polar codes and quantum RM codes, thus addressing the challenges of designing valid quantum polar codes without entanglement assistance and improving finite-size code performance. We test the proposed codes’ performance under successive cancellation list decoding, and find that they indeed provide performance improvements. This work will be presented by Keita at QEC 2025 and ITW 2025. The paper can be found here.
Information Theory of Multimode Optical Fiber
As an undergraduate student, I found the idea of using optical fiber modes as distinct spatial channels fascinating and this led me on an amazing journey, where I learned a lot from Professor Mansoor I. Yousefi about the physics and information theory of communication across optical fiber channels. My Bachelor’s thesis on the information theory of multimode optical fiber can be found here.

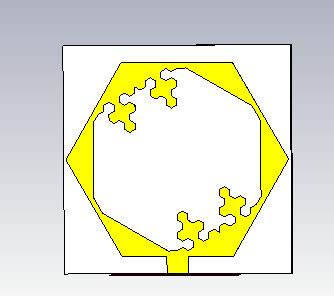
Antenna for Body Area Network
For the IEEE APS 2015 student design contest, I worked with Mustafa Mahmoud, Mohamed Atef, and Hassan Nassar, with our mentor Hany Fathy Hammad to design a power efficient wearable BAN system using an inkjet-printed fractal antenna. I worked on designing and simulating the antenna. The work resulted in the publication Novel CPW-fed fractal Sierpinski Arrowhead inkjet-printed antenna design.